In high-rise buildings, fast-moving elevators pose challenges such as atmospheric pressure impact, noise, and vibration. The noise and vibration generated by elevators can have negative effects on the health and well-being of residents and impact the comfort of a community. Therefore, solutions are needed to minimize elevator noise and vibration in high-rise buildings.
Through measuring the noise levels of high-rise buildings that have implemented solutions, the noise levels have significantly decreased, especially in the frequency range >125 Hz. The findings of this study can serve as guidelines to mitigate noise and vibration issues from elevators during the design and construction of high-rise buildings to ensure sustainability.
Elevator Noise in High-Rise Buildings
Classification of Buildings:
- Low-rise: 5 – 6 floors.
- Mid-rise: 7 – 15 floors.
- High-rise: 16 – 20 floors.
- Super high-rise: 21 – 49 floors.
Depending on the number of floors and households on each floor, the capacity and speed of elevators in each building vary. Elevator speed per floor:
| Floors | Elevator Speed (meters per minute) |
| <10 floors | 60 |
| 10 – 14 floors | 90 |
| 15 – 25 floors | 105 |
| 26 – 30 floors | 120 |
| 31 – 40 floors | 150 |
| >40 floors | 180 |
The changes in air pressure, noise, and vibration occurring as the elevator moves in high-rise buildings can cause discomfort for passengers and have negative effects on the living environment of nearby residents. According to the building standards of many countries, the characteristic noise level generated by living in an apartment building should not exceed 30 dB(A) in any bedroom or living room of the apartment.
The source of elevator noise
figure 1 below illustrates the pathways through which elevator noise and vibration generated in the elevator shafts of high-rise residential buildings are transmitted to apartments. Elevator noise and vibration occur primarily when the machinery operates in the machine room and machine room corridor. Noise emanates from various sources, including airborne noise transmitted as sound waves through the air, as depicted in the figure, as well as structure-borne noise transmitted through building components such as walls, partitions, and ceilings. These two types of noise are then transmitted to spaces requiring quietness, such as bedrooms and living rooms of apartments, continuously compromising the comfort of residents’ daily lives.
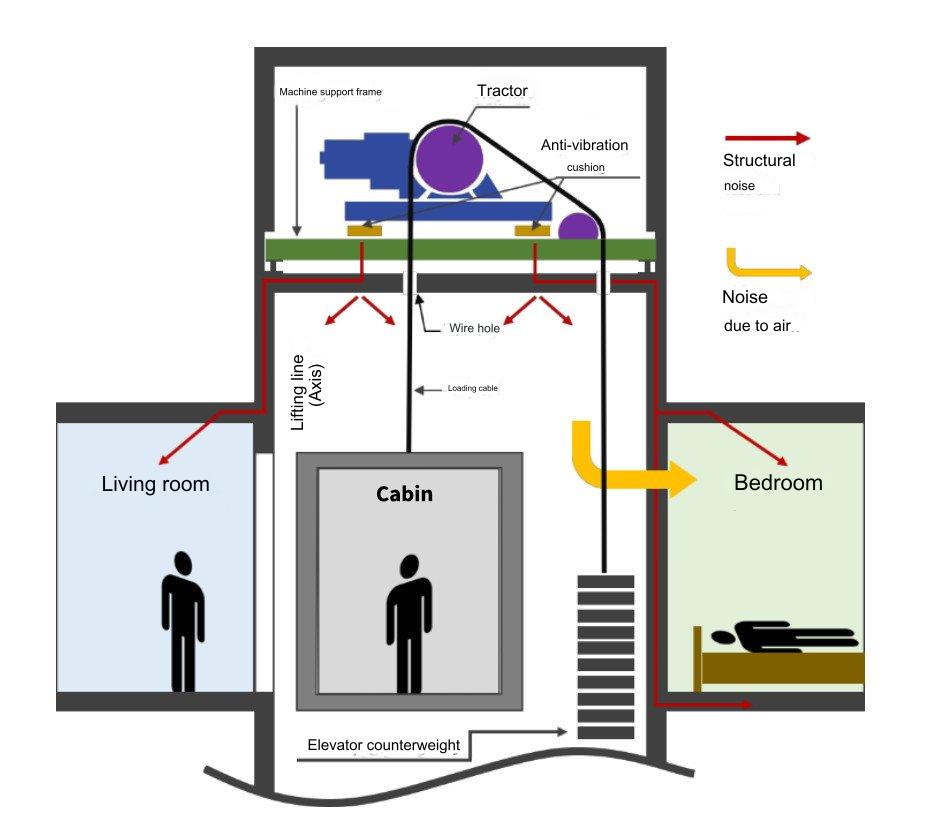
Elevator Noise Sources, Causes, and Types:
| Elevator Component | Source | Cause | Type of Noise |
| Machine Room | Motor | High-frequency rotation | Single-tone |
| Gear and Brake | Gearbox tooth frequency; Brake engagement and disengagement | Mechanical impact, shock, Friction | |
| Control Panel | Electrical control switch for elevator | impact | |
| Elevator Hoistway | Door | The operation of the non-axial door components | Friction |
| Elevator Rails and Guides | The rotation of the bearings; The rotation of the rollers; Passing through rail joints; Interaction between gears and cables | Single tone, mechanical impact & shock, friction | |
| Elevator | Sudden pressure surges; Air friction and narrow passages | Airborne noise transmission |
The table below provides details on the various pathways through which noise is generated from multiple sources and transmitted to residential units. Specifically, noise is transmitted through structures and via the air.
Vibration noise is generated by machinery in the machine room and transmitted to residential areas through structural components such as vibration isolators, machine frame, machine room floor panels, and machine room corridors.
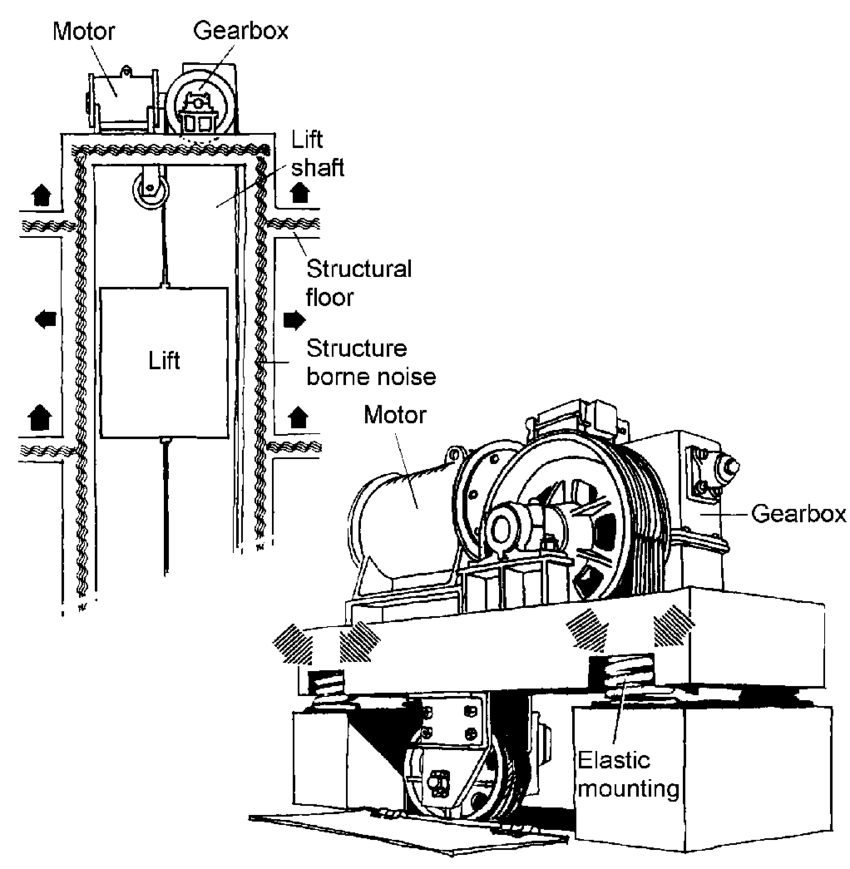
In addition, noise generated by the vibration of the elevator car during movement up and down is transmitted to residential areas through elevator guide rails, rail brackets, and elevator shafts.
Therefore, the structural components of the elevator system and the noise transmission components need to be designed and implemented accurately to minimize noise. Additionally, elevators require special noise and vibration reduction solutions.
| Description | Source | Transmission Path |
| Structural noise | Machine room | Machinery → Vibration damper → Machine frame → Machine room floor → Elevator corridor wall → Apartments |
| Machine room corridor | Elevator guide rail → Guide rail → Guide rail bracket → Elevator corridor wall → Apartments | |
| tiếng ồn trong không khí | Machine room | Cable holes → Elevator corridor wall → Exterior ventilation of apartment → Nearby residents’ windows → Residential buildings |
| Machine room corridor | Elevator corridor → Elevator corridor wall → Apartments |
The airborne noise generated inside the machine room is transmitted through the wire holes as shown in Figure 1, passing through the elevator shaft wall to the residential area; furthermore, airborne noise is transferred to the residential area through ventilation holes and windows of neighboring residential buildings.
Airborne noise generated by the elevator shaft is transmitted to residential areas through the elevator shaft wall. Additionally, there may be airborne noise generated during the movement up and down inside the elevator shaft, which can be easily controlled by thick reinforced concrete (RC) walls (>200 mm) and soundproof concrete without cracks.
Solutions for High-Rise Elevator Noise Reduction
To address the issues of elevator noise and vibration in buildings, numerous studies on mechanical solutions have been conducted, with solutions presented from the perspective of design and construction, typically aimed at residential buildings with fewer than 10 floors.
Therefore, to reduce elevator noise and vibration in buildings with elevators running at speeds >90 m/minute, solutions consider the characteristics of high-speed elevators and the floor plan of high-rise buildings, along with the use of high-quality soundproofing materials, vibration-damping panels, noise-reducing panels, and so forth.
These material panels would be positioned in locations such as elevator doors, machine rooms, gearbox enclosures, elevator shafts, and other areas that may generate noise.
Furthermore, proper design can also help mitigate noise. Designing elevator shafts and elevator components to ensure there are no gaps or openings, and using soundproof elevator doors are some design measures that can be applied.
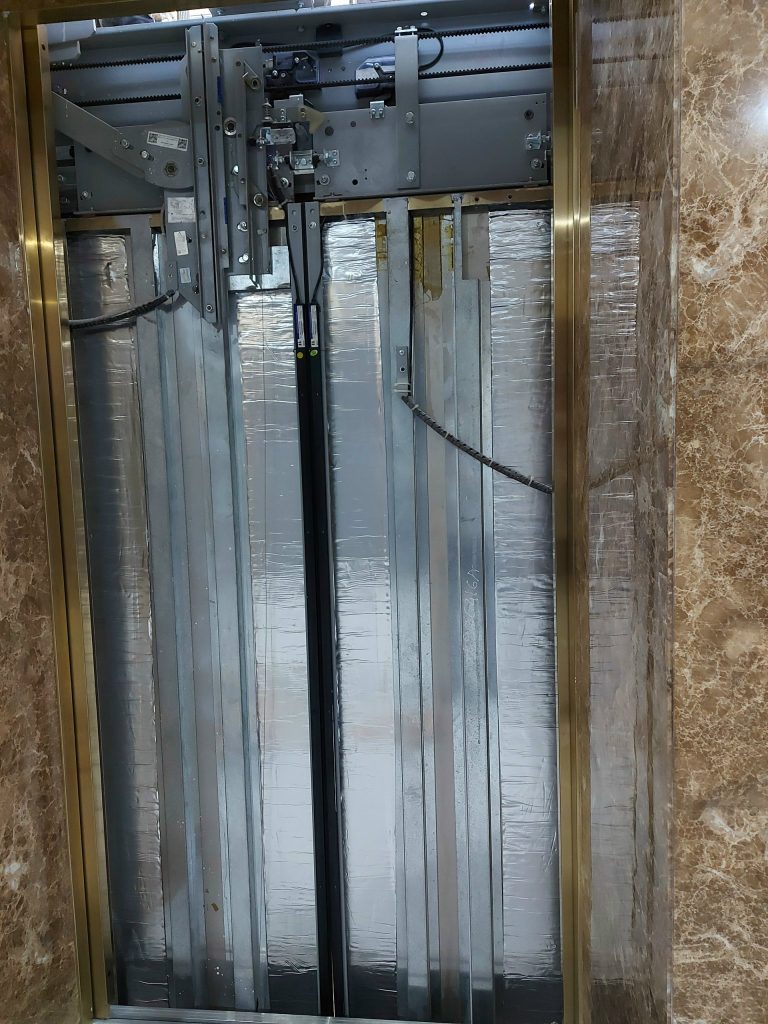
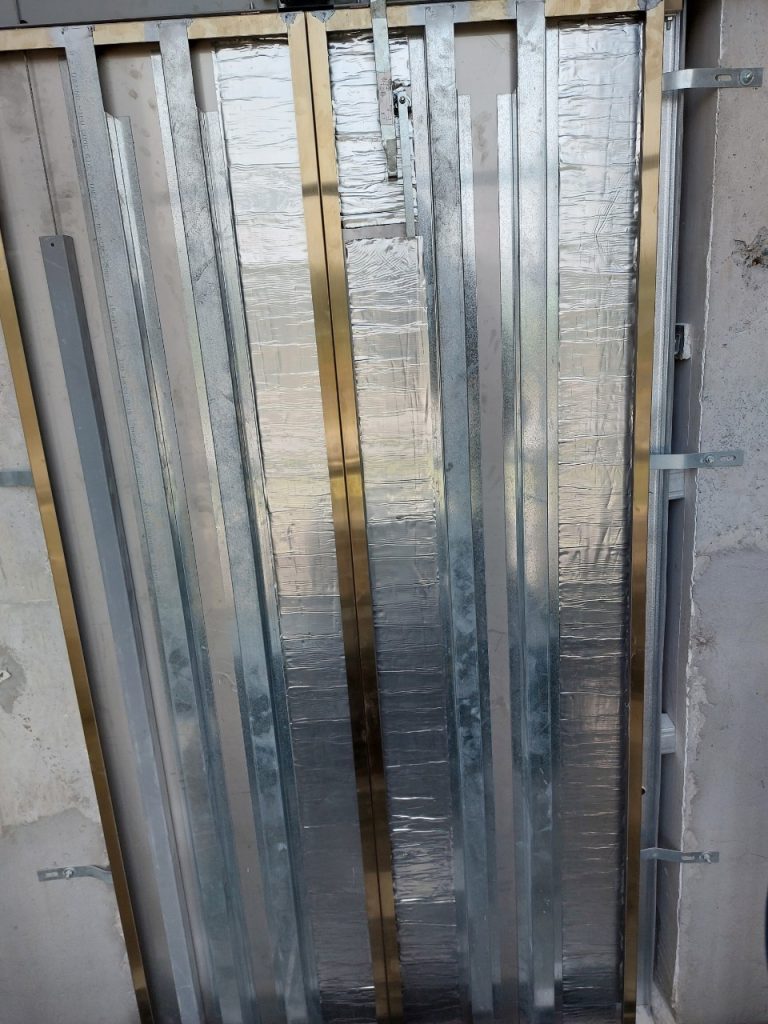


Consulting on Noise Reduction Solutions for High-rise Elevators

- Related article: Solutions for vibration and noise reduction in elevators
Hitta JSC is a leading provider of noise and vibration control products and solutions in Vietnam, renowned for its Hitta brand products. We have successfully implemented solutions for elevators, as well as luxury buses, coaches, and limousines. Hitta’s noise and vibration control products are trusted by hundreds of clients nationwide, and this number continues to grow. Contact us today for expert advice.
- ☎️ Hotline: 090.8611.011
- ✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn

