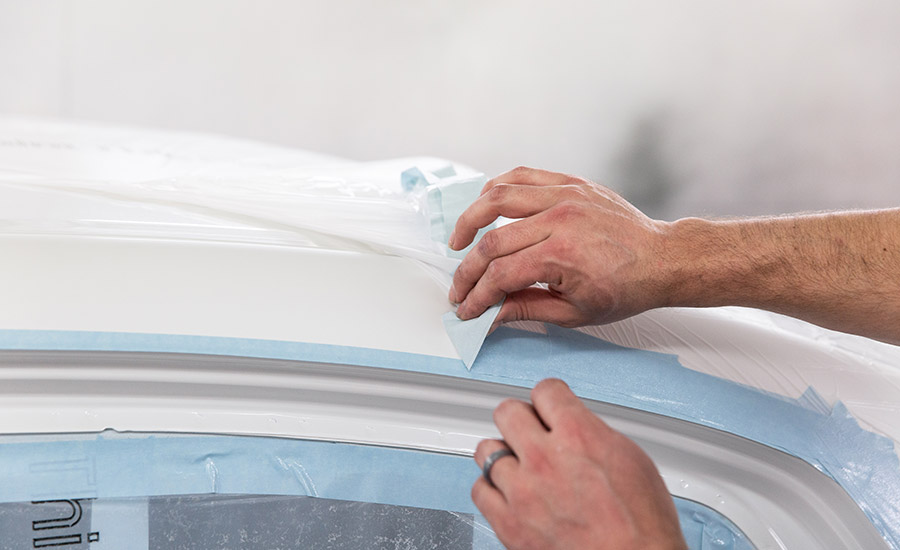
Masking tape, also known as surface protection tape or barrier tape, is a type of adhesive tape characterized by its light adhesion, easy roll-out and tear, and ability to be applied to various surfaces and removed without leaving any traces or causing damage.
The gentle adhesion and low tackiness of masking tape make it ideal for numerous applications, both in professional and non-professional settings..
Structure of Masking tape
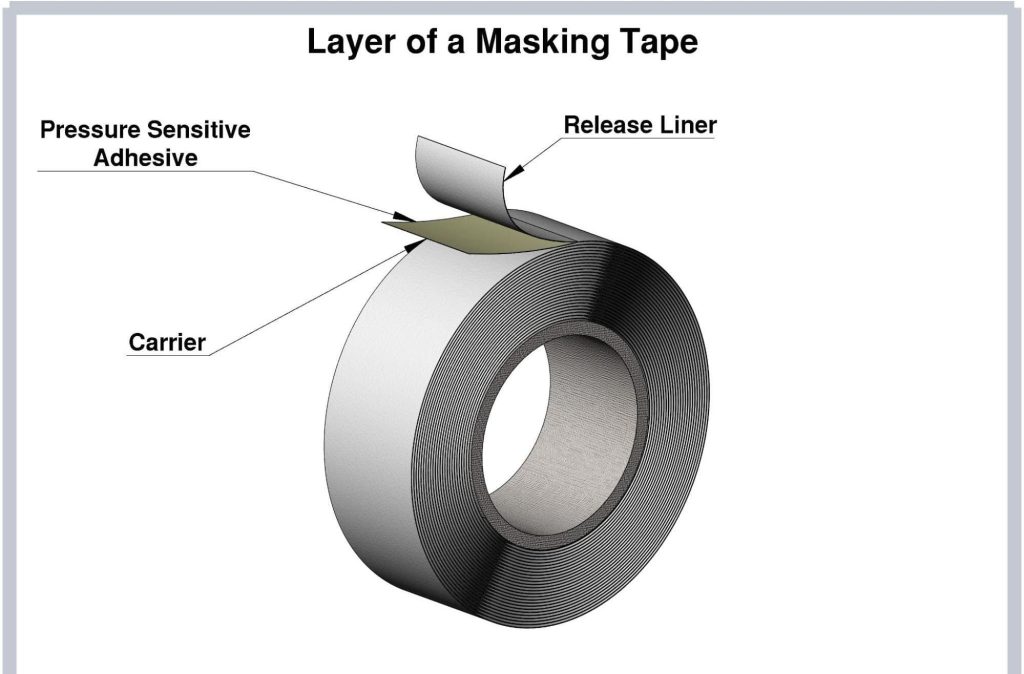
Masking tape consists of three layers: the carrier layer, the adhesive layer, and the outer protective layer (release liner).
Carrier layer
| Ceramic | The tape features a ceramic backing layer suitable for extreme heat conditions and is typically a proprietary blend of alumina-boria-silica fibers or some other types of ceramic fabrics. |
| Foam | Foam polyolefin adhesive tapes comprise an adhesive layer protected by a backing in the form of a tape, film, or thin laminate layer. |
| Foil | “foil backing is highly reflective and heat-resistant. They typically have an aluminum backing, reinforced with aluminum or lead. |
| Glass | They are similar to fabric carrier layers but reinforced with glass beads or glass fibers to enhance heat resistance up to 148°C. |
| Polyimide | Polyimide film maintains excellent physical, mechanical, chemical, and electrical properties in various physical environments. |
| PVC/vinyl | By employing a vinyl backing layer to enhance resistance against biological and chemical damage, as well as improving processability. PVC is also relatively inexpensive. |
| Paper | The paper backing layer is widely used in masking tape due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of manufacturing and distribution, and is typically kraft paper, washi, or crepe paper. |
| PET/polyester | The polyethylene terephthalate/polyester backing layer exhibits high solvent resistance and has excellent properties of aging resistance and transparency. |
| Fluoropolymer | The fluoropolymer backing layer provides excellent chemical resistance as well as water and dirt repellence. The inert nature of this backing layer prevents unintended adhesion. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) are common backings for adhesive tapes. |
The backing layer is made from various materials including paper (most common), polyester, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polyamide.
Materials like PVC, polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are thin and exhibit excellent tear resistance.
The uniformity of each type of plastic backing material ranges from soft to rigid, each designed to meet the needs of different applications. They are widely used as surface protection or packaging materials.
Fabrics such as cotton and PET have suitable mechanical properties for covering cracks and packaging. Different types of fabric backing layers have high tensile strength but may tear easily. PET backing layers are highly resistant to tearing or ripping.
Adhesive layer
| Acrylic | Acrylic-based adhesive achieves maximum adhesion almost instantly upon application, providing strong, durable bonding without the need for priming, and offering excellent indoor and outdoor durability. |
| None | Tapes without adhesive layer. These tapes possess self-adhesive properties, relying on high friction coefficient to maintain adhesion. |
| Rubber/resin | The adhesive with a high rubber-based chemical structure features highly flexible bonds based on compounds like butadiene-styrene, butyl, polyisobutylene, or nitrile. |
| Silicone | Silicone-based adhesive has high flexibility and excellent heat resistance (up to 315°C). Although available in pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) applications, some silicone adhesives may require ventilation or UV or EB radiation for processing. |
All types of masking & surface protection tapes feature an adhesive layer possessing three characteristics: cohesion, adhesion, and tack.
The four main types of adhesives are rubber/resin, synthetic rubber, acrylic adhesive, and silicone-based rubber/resin, with the latter being the oldest type introduced in the 1920s.
Rubber/resin adhesive
Rubber/resin adhesive is made from natural rubber requiring resin additives to form the adhesive. It has high initial tack and adheres tightly to any surface. Rubber adhesive provides flexible bonding based on compounds like butadiene-styrene, butyl, polyisobutylene, or nitrite.
Properties of rubber/resin adhesive for masking tape:
- High initial adhesion.
- Low tendency for adhesive build-up.
- Good tensile strength.
- Moderate heat resistance.
- Excellent solvent resistance.
- Moderate UV light resistance.
- Average durability.
Synthetic rubber adhesive
Synthetic rubber adhesive utilizes synthetic rubber instead of natural rubber. They differ from natural rubber in having higher adhesion and shear resistance, making them ideal for creating tight bonds.
Properties of synthetic rubber adhesive for masking tape:
- High adhesion.
- High shear resistance.
- Resistance to aging.
- Good tackiness.
- Creates tight bonds.
Acrylic adhesive

Acrylic-based masking tape
Acrylic adhesive is made from acrylic polymer and is known for its flexibility, fast drying, and excellent heat resistance. It is widely used in masking tapes due to its ability to adhere to various surfaces. The flexibility of acrylic adhesive makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring vibration resistance and flexibility. With its stability against oxidation, acrylic adhesive maintains its bond for many years and provides protection against UV rays.
Properties of acrylic adhesive for masking tape:
- Good initial adhesion.
- Gradual build-up of adhesive tackiness.
- High tensile strength.
- Excellent heat resistance.
- Outstanding solvent resistance.
- Excellent UV resistance.
- Good durability.
- Long-lasting bond.
Silicone adhesive

Masking tape with Silicone adhesive
Silicone-based adhesive is made from silicone polymer, offering flexibility and excellent heat resistance. The bonds formed by silicone adhesive can withstand temperatures up to 315°C while maintaining flexibility and resisting the effects of water and chemicals. Among various types of masking tapes, silicone-based masking tape is the most expensive.
Properties of silicone-based adhesive for masking tape:
- Heat resistance.
- Chemical stability.
- Insulation.
- Abrasion resistance.
- Weather resistance.
- Ozone resistance.
Release liner layer
This layer ensures that the tape rolls and layers do not stick to each other and allows for easy separation of the tape from the roll. This layer can take various forms such as glassine paper, coated paper, polyethylene film, or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film. The release liner is crucial in automated applications where the adhesive tape needs to be quickly separated from the roll.
Common types of masking tape
| Painter’s masking tape is a specially manufactured tape designed to assist with painting tasks. It is used to prevent paint from covering different color areas to create contrast, or to avoid paint sticking to undesired areas. This type of tape is commonly used in decorative detailing. Some specialty painter’s tapes have a thick viscosity coating, such as lacquer and polyurethane. Other popular types of painter’s masking tapes are used for automotive painting applications, where the adhesive properties are altered based on the application area. |
| Plating tape is used to protect sensitive components from unwanted metal deposition during electroplating or to create metal oxides during the anodizing process. These tapes must withstand acid, chemicals, and harsh temperatures. |
| Abrasive blasting tapes are used to cover components during sandblasting, shot blasting, or other surface finishing processes using rough treatment methods. The rubber or elastomer lining provides abrasion resistance for the covered areas. |
| High-temperature masking tape is a type of adhesive tailored for welding, hard soldering, and soft soldering applications. This is particularly useful for processes like wave soldering, and this type of tape usually dissolves in water and has low static electricity. Welding tape uses a welding alloy layer on both sides of the tape, which is then coated with an adhesive and carrier. |
| Thermal spray tapes resist impact and heat from processes like plasma spraying, wire arc spraying, or oxyfuel. These tapes also have good abrasion resistance and are easy to release from the adhesive. |
Applications of Masking tape
In addition to its role in preventing overspray and creating clean paint lines, masking tape also serves as a protective layer during coating application, bundling parts, covering cracks, and joining surfaces.
Masking tape is essential and indispensable, playing a vital part in industrial processes where the goal is to expose a portion of the surface and shield surfaces where processing is to be avoided. Processes like E-coating, wet painting, and powder coating all require a high-performance masking tape with adhesive that can adhere to difficult substrates and withstand heat and chemicals while still providing easy and clean removal.
Automotive industry

In the automotive industry, masking tape is highly important for high-temperature masking, paint repairs, and two-tone painting. The tape must meet high requirements to ensure product quality and also needs to be flexible, heat-resistant during baking, and removable without damaging the work.
Construction

In the construction industry, masking tape is used for protection during painting and sealing, including specialty tapes for stucco surfaces and flat tapes for floor protection.
electronics industry
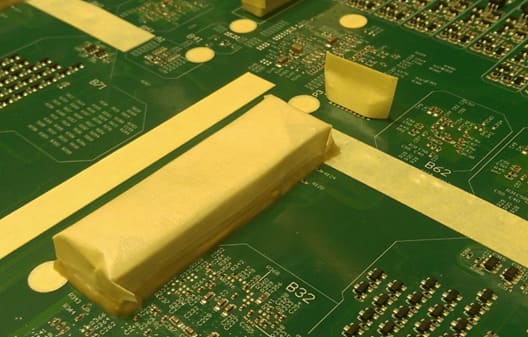
There are various uses of masking tape in electronic devices, including wrapping and splicing cables as well as covering components during soldering.
It is used to connect electrical cables and add an extra layer of insulation to cover exposed wires and waterproof junctions. In the manufacturing of circuit boards, specially produced masking tape is used to cover areas of the board during coating.
Painting
Different industries enhance the appearance of their products through painting. To ensure paint durability and prevent peeling, it is baked at high temperatures after drying.
Powder coatings are also applied, cured at high temperatures to flow and form a skin on the product.
Masking tape used for industrial applications, such as oven painting, must be able to withstand high-temperature conditions with temperatures reaching up to 370°C. The types of labeling masking tapes for these production conditions include masking tape backings of polyester, crepe paper, aluminum foil, and yellow vinyl, each capable of withstanding harsh and challenging conditions.
Advantages of masking tape
Protection, Shielding: The primary function of masking tape is to shield surfaces from excessive spray, leaks, and potential damage. The use of masking tape ensures that only the surfaces requiring treatment will be processed.
High Applicability: One of the reasons masking tape is popular is its ease of use. A small amount of pressure activates the adhesive upon contact with any surface. This property holds true for industrial masking tapes used in surface protection during coating, priming, and painting as well as for DIY projects.
Ease of Removal: Once a project is completed and the applied materials have dried, it’s crucial that the protective masking tape can be easily removed without leaving residue. This is particularly important for new cars, boats, and airplanes where smooth surfaces are necessary. The tackiness of masking tapes allows them to adhere immediately to a surface and form a tight bond.
The second step in the process is the efficient removal of the tape, which happens easily. With minimal force, all types of masking tape can be pulled away, leaving clean straight lines separating treated surfaces.
Versatility: Masking tape is a tool designed to fit the needs of various applications, from stove enamel heat treatment to mold protection during painting. It’s this versatility that has expanded its use from a house painter’s toolbox to automobile production lines.
Adding to its versatility are the many varieties of masking tape with different backings, adhesives, widths, and thicknesses, each with the same characteristics and properties for different applications. The industrial use of masking tape has made it a time-saving tool that prevents errors and damage.
Cost-effectiveness: The low cost and high reliability of masking tape are among its most appealing features, especially for industrial masking tape. The main cost of masking tape is the adhesive used for bonding with a surface, with silicone-based masking tape being one of the more expensive types, though still much less than other protective measures.
Recyclability: Certain segments of modern production are concerned with sustainability and environmental protection. Masking tape fits comfortably into the initiatives supported by companies concerned with compliance with these factors.
How to Choose the Right Masking Tape for Your Application
There are 2 factors to consider when choosing the right masking tape:
- SIZE – When it comes to selecting the best masking tape for your needs, size is one of the most important factors to consider. When considering size, besides length, width, and thickness are also taken into account. Narrower tape widths make it much easier to mask off small areas, corners, and tight spaces. On the other hand, wider tapes are best suited for masking off larger areas and provide additional protection against small paint drips or splatters.
- ADHESION – When purchasing any type of tape, it’s important to check how adhesive it is. This is beneficial as it allows you to choose a less adhesive tape when working with delicate surfaces or newly painted materials. Additionally, a higher level of adhesion may be needed when applying tape to textured surfaces or in harsh temperature conditions.”
Purchase masking tape
Hitta specializes in providing various types of adhesives and specialty tapes for both industrial and commercial sectors. Contact us for the most effective solutions with the lowest cost.
- ☎️ Hotline: 0565 33 68 79
- ✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn

