When it comes to adhesive tapes, adhesives, and PSA (Pressure Sensitive Adhesive) bonding agents, there is a fundamental principle that determines their bonding capability, which is surface energy
In this post, we will discuss surface energy and solutions for bonding difficult or low surface energy materials.
What is surface energy?
Surface energy is the excess energy present on the surface of a solid material. To visualize this, imagine a cubic block. At the center of the cubic block, each individual molecule is surrounded by other molecules in the x, y, and z planes. These molecules interact with each other and balance out in their interactions, forming what is known as cohesive strength. However, at the surface, the molecules are not completely surrounded and only interact with the molecules adjacent to and below them. This imbalance in molecule interactions results in surface energy.
- Low Surface Energy (LSE)
- High Surface Energy (HSE)

Adhesion is determined by the molecular attraction forces between materials. The strength of these attraction forces depends on the surface energy of the material.
- High Surface Energy (HSE) = Strong molecular attraction forces.
- Low Surface Energy (LSE) = Weak molecular attraction forces.
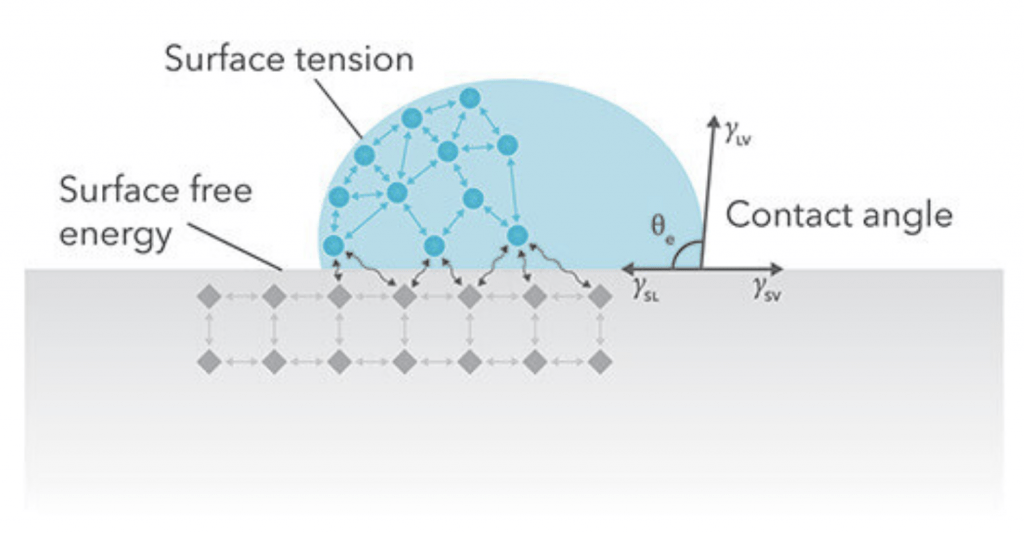
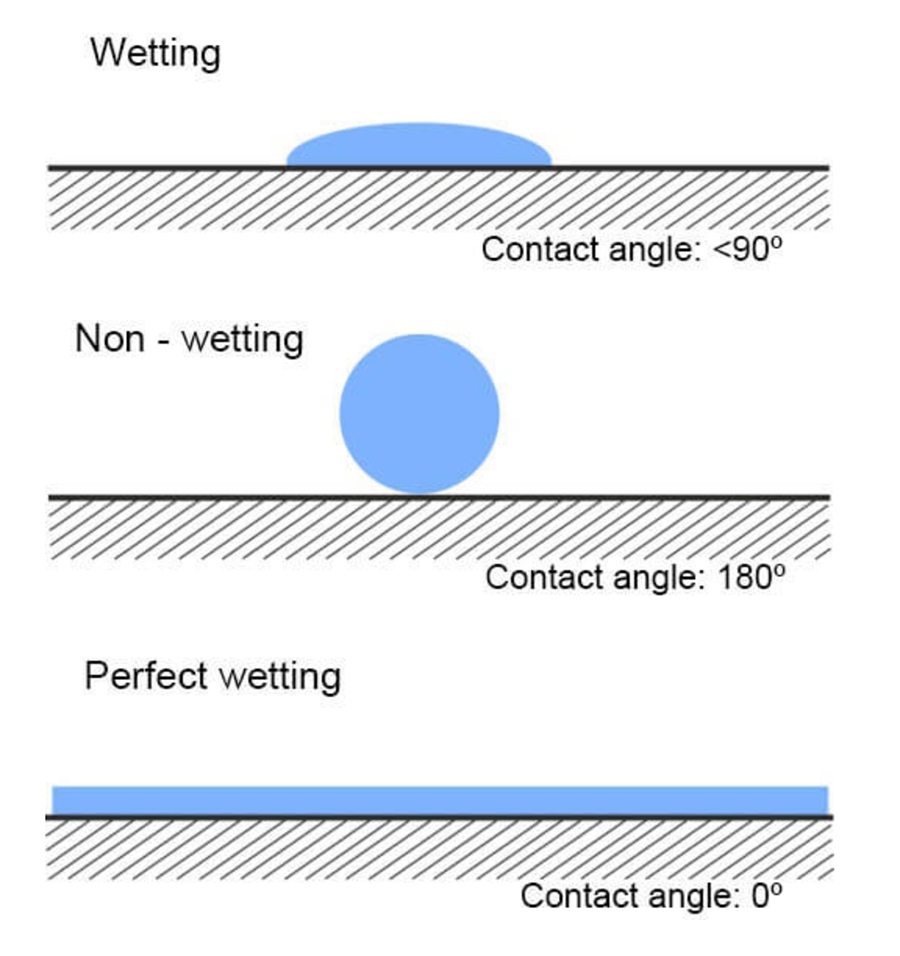
The simplest way to identify whether a material has low or high surface energy is to check its wetting or spreading properties with water. When water droplets are placed on the surface, they will form a contact angle, which reflects the surface energy of the material. If the water droplets spread out, it indicates that the material has high surface energy (HSE). Conversely, if the water droplets bead up and do not spread out, it suggests that the material has low surface energy (LSE). To visualize this concept better, refer to the next section of the article.
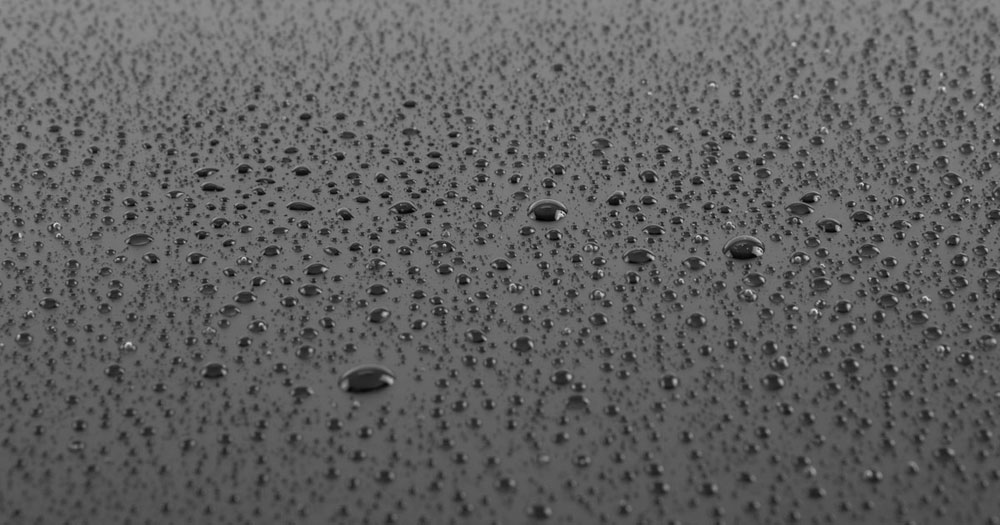
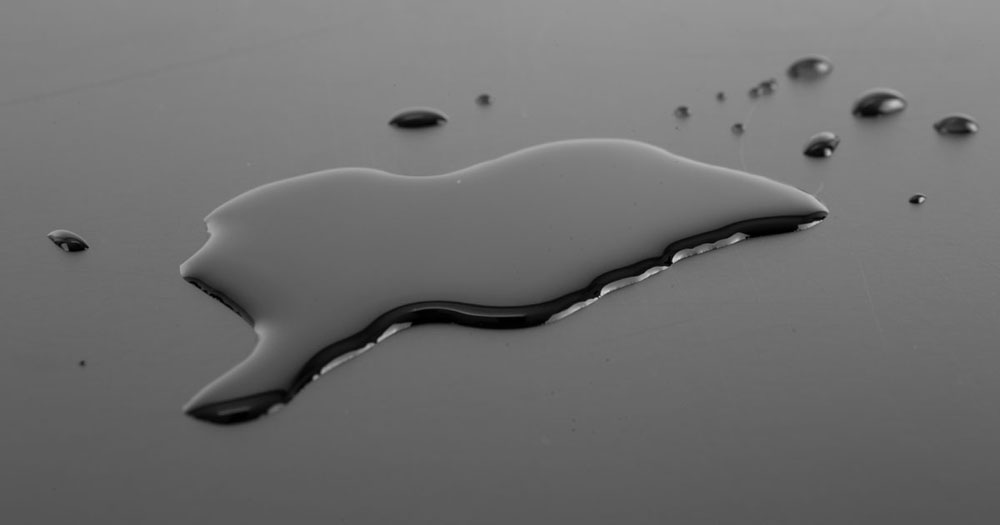




Typically, surface energy is measured in a unit called “dynes,” where 1 dyne/cm is equivalent to 1 mJ/m.
When a water droplet is placed on a surface, it will spread to some extent. In theory, if the surface energy is zero, the water droplet will form a perfect sphere. Conversely, if the surface energy is infinitely high, the droplet will form a completely uniform film. We can measure the angle formed at the edge of the droplet. (For a sphere, this angle will be 0°; for a uniform film, it will be 180°.)
Classification of Surface Energy
Surface energy of materials can be classified into three groups: high, medium, and low surface energy.
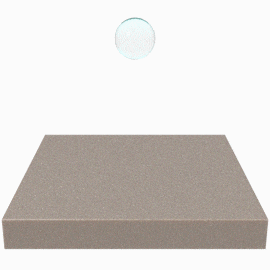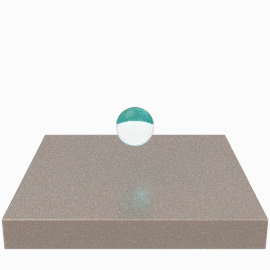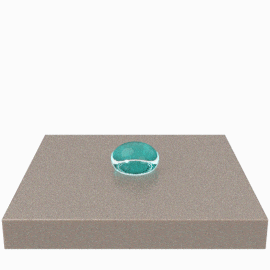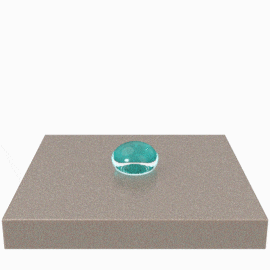
High Surface Energy (HSE)
Molecules on the surface are strongly attracted to each other, even to liquid molecules. Therefore, these materials are relatively easy to bond. High Surface Energy (HSE) materials are categorized by energy levels ranging from 100 to 1000 dynes/cm and include many metals and glass.

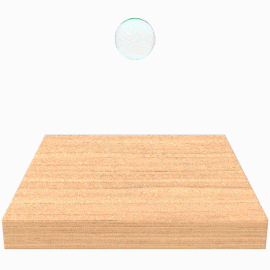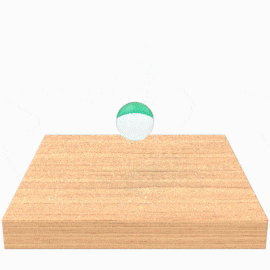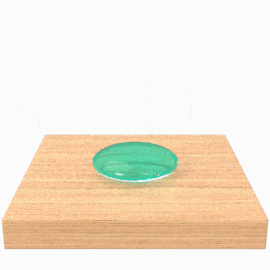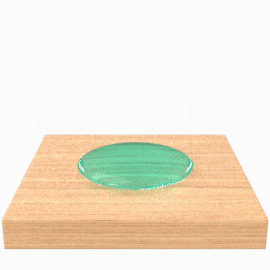
Medium Surface Energy (MSE)
These are materials typically ranging from 36 dynes/cm to about 300 dynes/cm. Many types of plastics manufactured have surface energies within this range, as well as natural materials such as wood, stone, or concrete.
Low Surface Energy (LSE)
The molecules on the surface of low surface energy materials have relatively low attraction forces. There is very little attraction to any molecules, especially adhesive molecules. Materials with surface energies below 36 dynes/cm are considered low surface energy and are very difficult to bond. They include polyolefin plastics such as polypropylene and polyethylene as well as non-stick surfaces like polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Surface energy of some common materials:
High Surface Energy (HSE) materials:
| Material | dyn/cm |
|---|---|
| Copper | 1,103 |
| Stainless Steel | 700-1,000 |
| Aluminum | 840 |
| Zinc | 753 |
| Tin | 526 |
| Glass | 250-500 |
| Nylon | 46 |
| Polyester (PET) | 43 |
| ABS Plastic | 42 |
| Polycarbonate | 42 |
Low Surface Energy (LSE) materials:
Here’s the data table translated into English:
| Material | dyn/cm |
|---|---|
| PVC | 39 |
| Acrylic | 38 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 31 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 29 |
| PTFE Fluoropolymer (Teflon®) | 18 |
Bonding low surface energy materials:
It is evident that plastic materials often have low surface energy (LSE), making bonding challenging for many industries. Adhering to plastics such as ABS (commonly used in automotive and bus industries), PP, and PVC poses a significant challenge. The double-sided tape (or high-strength adhesive tape) provided by Hitta effectively addresses this challenge, providing long-lasting results where other solutions may require additional support.
- Hiita là Nhà phân phối BowTape độc quyền tại Việt Nam
- Hitta JSC Là Nhà Phân Phối 3M chính thức tại Việt Nam
These tape solutions bond synthetic materials and low surface energy plastics (LSE) without the need for additional primers, thus increasing productivity and reducing the use of harmful chemicals. Excellent durability and resistance to various temperature levels ensure the highest durability and reliability for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Tìm hiểu về băng keo 2 mặt
- Tại sao nên sử dụng băng keo cường lực?
- Giải pháp băng keo cường lực
- Băng keo cường lực cho thang máy
Adhesive tapes provide a flexible bond that allows for thermal expansion up to three times its thickness, making it ideal for joining different materials. Double-sided tape (or high-strength adhesive tape) demonstrates excellent dynamic stress performance. By leveraging its strong adhesion capability on low surface energy materials, you can use lighter and thinner materials, enabling a diverse range of applications to achieve breakthrough improvements in form and function, supporting durability, aesthetics, and weight reduction.
Recent advancements in adhesive technology offer designers and manufacturers new assembly options beyond traditional mechanical assembly methods with drawbacks such as inability to join different materials (welding), poor aesthetics, material surface damage, and susceptibility to corrosion when used outdoors (rivets, bolts, screws). Double-sided tape/high-strength adhesive tape can be applied to various materials, including synthetic materials and low surface energy plastics (LSE), optimizing design and enhancing flexibility in the production line.
If you need expert advice, please contact Hitta for the best support.
☎️ Hotline: 090.8611.011 (Mr. Dương)
✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn
Here are some double-sided tape and high-strength adhesive tape products capable of adhering to low surface energy (LSE) materials:
-
 Bow Tape 110 (0.11 mm)
Bow Tape 110 (0.11 mm) -
 Bow Tape 110QJB (0.16 mm)
Bow Tape 110QJB (0.16 mm) -
 Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 723G (2.3 mm)
Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 723G (2.3 mm) -
 Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 730W (3.0 mm)
Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 730W (3.0 mm) -
 Acrylic Foam tape with LSE coating – Bow Tape 708GLM (0.8 mm)
Acrylic Foam tape with LSE coating – Bow Tape 708GLM (0.8 mm) -
 Bow Tape PE foam Tape 398A (0.8 mm)
Bow Tape PE foam Tape 398A (0.8 mm) -
 Bow Tape PE foam tape 398EW (1.0 mm)
Bow Tape PE foam tape 398EW (1.0 mm) -
 Bow Tape 391W (1.6 mm)
Bow Tape 391W (1.6 mm) -
 Bow Tape 300NHK
Bow Tape 300NHK -
 Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 711BH
Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 711BH -
 Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 715B (1.5 mm)
Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 715B (1.5 mm) -
 Bow Tape 3510PP (0.1 mm)
Bow Tape 3510PP (0.1 mm) -
 Bow Tape 550 (0.17 mm)
Bow Tape 550 (0.17 mm) -
 Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 7025THH
Acrylic Foam Tape – Bow Tape 7025THH -
 Bow Tape 1750L (0.05 mm)
Bow Tape 1750L (0.05 mm) -
 Bow Tape 590 (0.09 mm)
Bow Tape 590 (0.09 mm) -
 Bow Tape 710SF (1.0 mm)
Bow Tape 710SF (1.0 mm) -
 Bow Tape 3510B
Bow Tape 3510B -
 Bow Tape 3505B
Bow Tape 3505B -
 Bow Tape 716GS
Bow Tape 716GS -
 Bow Tape 706BH (0. 6mm)
Bow Tape 706BH (0. 6mm) -
 Transparent Reinforcement Tape Bow Tape 710T (thickness 1.0 mm) Self-Adhesive
Transparent Reinforcement Tape Bow Tape 710T (thickness 1.0 mm) Self-Adhesive -
 Bow Tape 110QJ (0.16 mm)
Bow Tape 110QJ (0.16 mm) -
 Bow Tape 704WE (0.4 mm)
Bow Tape 704WE (0.4 mm) -
 Bow Tape 706BH (0.6 mm)
Bow Tape 706BH (0.6 mm) -
 Bow Tape 708GSX (0.8 mm)
Bow Tape 708GSX (0.8 mm) -
 Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 711G (1.1mm)
Acrylic Foam Tape Bow Tape 711G (1.1mm)
