What is heat-resistant adhesive?
Heat-resistant adhesive is a type of adhesive capable of withstanding high temperatures. The strongest heat-resistant adhesives can withstand temperatures above 300°C. Heat-resistant adhesives must be able to bond various types of materials, typically including metals, ceramics, rubber, and glass. Some adhesives also work effectively on plastic materials.
Heat-resistant adhesives include various types such as cyanoacrylates, epoxies, acrylics, silicone, and urethane. Each type has its own unique characteristics, making it more suitable for specific tasks. Heat-resistant adhesives are commonly used in the following applications:
- Ovens, stoves, and furnaces.
- Automotive interiors.
- Engines.
- Industrial applications.
- Joints in exhaust systems and heating systems.
High-temperature adhesive compliant with European standards
Bostik 7003 adhesive is a high-temperature adhesive, fire-resistant adhesive that can withstand temperatures from -40°C to +120°C while maintaining a permanently elastic joint. This adhesive meets European standard EN 45545 and is widely used in the assembly of rail vehicles in Europe, especially in France.
Below is a video testing the heat resistance and fire resistance of Bostik 7003:
Applications of Bostik 7003 high-temperature adhesive:
- Flexible bonding and seam sealing joints, such as bus, caravan, and truck assemblies.
- Bonding and seam sealing of sunshade systems.
- Joints in bus, train, and truck roof systems.
- Aluminum or polyester profile joints.
- Floor system joints.
- Joints of polyester components on metal frames.
- Seam sealing of welds.
Recommended products:
Purchase high-quality heat-resistant adhesive at competitive prices
Hitta specializes in providing industrial solutions and is an authorized distributor of Bostik. Please contact us for detailed consultation and to purchase products at the best prices:
 Hotline: 056 533 6879
Hotline: 056 533 6879 Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn
Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn
Below are some technical specifications that customers need to consider to better understand the selection of heat-resistant adhesives & high-temperature adhesives:
What is the difference between heat-resistant adhesive and high-temperature adhesive?
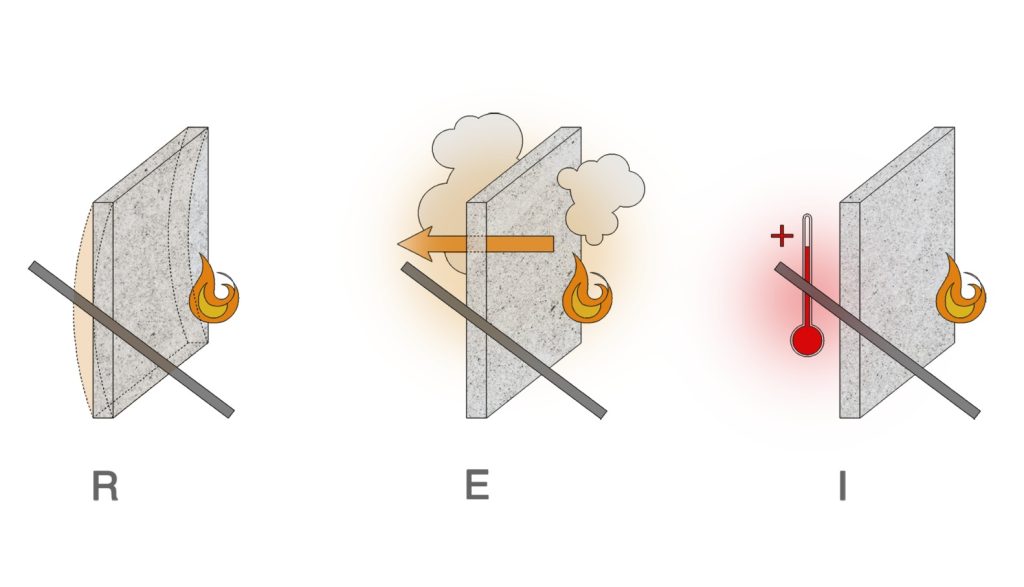
Some characteristics of heat-resistant adhesive to consider for classification include:
- Temperature resistance/application temperature.
- Thermal expansion coefficient.
- Thermal cycling – Thermal shock.
The reason why some adhesives are listed as high-temperature adhesives when they can withstand only 150°C, while others are classified as high-temperature adhesives when they can withstand temperatures of 300°C or higher, depends on the adhesive technology. For example, a standard one-component cyanoacrylate adhesive may withstand temperatures up to 150°C, so a one-component cyanoacrylate adhesive that can withstand temperatures of 230°C would be classified as a high-temperature adhesive.
In contrast, ethyl cyanoacrylate-based adhesives typically withstand temperatures up to 82°C, while high-temperature cyanoacrylate adhesives can withstand temperatures up to 250°C.
Organic adhesives such as cyanoacrylates, epoxies, acrylics, and urethanes, which cure with ultraviolet light, typically degrade at temperatures between 250 and 300°C.
Inorganic adhesive binders such as ceramic cyanoacrylate adhesives can withstand temperatures up to 650°C, while silicone adhesives can exceed 350°C.
Thermal expansion coefficient
The intrinsic ability of a heat-resistant adhesive to resist degradation due to high temperatures is just one aspect of a complex set of conditions. Heat-resistant adhesives may soften as the temperature increases. This can be an additional benefit because the adhesive can absorb stresses related to different coefficients of expansion and contraction.
However, when designing heat-resistant adhesives for use in high-temperature applications, it is best to check the durability of the joint at the required temperature.
Application temperature
The application temperature is the temperature at which the adhesive can be used and is typically listed on the adhesive. Factors affecting the actual application temperature of any joint with heat-resistant adhesive include:
- Adhesion to bonded substrates.
- Bonding area.
- Rate of temperature change.
- Load or stress on the joint.
- Filling gaps with adhesive.
- Coefficient of expansion of the two substrates.
- Time at high temperature.
Most heat-resistant adhesives can withstand temperatures higher than the temperature listed as the application temperature for short periods, providing high adhesion to the substrate and stress resistance.
Heat Cycle / Thermal Shock
Many applications require joints to be heated and cooled repeatedly. When two components are joined together using mechanical means, microcracks can form along the thermal cycle or stress-induced cracks in the substrate.
Therefore, stress-absorbing adhesives can eliminate substrate degradation. Many adhesives are designed to withstand thermal cycles with greater flexibility, thereby absorbing stresses related to the expansion and contraction of the two components.
The rate of temperature change can be a significant factor in determining the success of a bond in resisting damage. Because thermal shock is a rapid temperature change that will affect the adhesive’s heat resistance.
What to keep in mind when purchasing heat-resistant adhesive?
When purchasing heat-resistant adhesive, besides considering its ability to withstand high temperatures, there are several other factors you should take into account:
- Resistance to temperature changes: Only some types of heat-resistant adhesives can withstand continuous exposure to high temperatures and temperature fluctuations.
- Curing time: Varies significantly among different types of adhesives.
- Viscosity: Heat-resistant adhesives with higher viscosity are thicker. This makes them more suitable for vertical applications, avoiding dripping.
- Compatibility: The adhesive must be compatible with the materials you intend to bond.
- Shock and vibration resistance: Essential when bonding parts that may undergo movement.
Other solutions you might be interested in:


