Consulting on purchasing suitable structural adhesives, meeting standards and regulations in Vietnam. Assisting customers in optimizing efficiency and cost savings.
Industries worldwide are utilizing modern types of structural adhesives. The bonding techniques of structural adhesives have surpassed traditional assembly methods such as riveting and welding, due to their numerous diverse benefits.
Today, one or two types of structural adhesives are applied in most consumer products. From start to finish, structural adhesives have supported numerous OEM tasks that require the most intricate and innovative approaches to streamline product lines, maximize process efficiency, and enhance finished product quality.
Structural adhesives versus traditional methods
Structural adhesive solutions are not only faster for assembly, but also stronger and more reliable compared to mechanical fasteners such as bolts, rivets, and welding. With many benefits and few drawbacks, structural adhesives are an excellent choice for many manufacturers.
Below is a comparison of structural adhesives with traditional methods, with a plus sign (+) representing the advantage and a minus sign (-) representing the disadvantage of each method.
Structural adhesives
+ Strong bond.
+ Low elastic modulus.
+ Corrosion protection.
+ Non-oxidizing.
+ Bonds with various materials.
+Stable over a wide temperature range.
+ Vibration resistance.
+ Provides a tight seal.
+ No visible joints or irregularities.
– Difficult to rework.
– Requires adequate bonding surface preparation.
– Susceptible to chemical activation.

Bolt
+ Fast.
+ Bonds different materials.
+ Removable.
– Stress concentration at bolt location.
– Bolt head protrudes or sinks.
– Prone to fatigue.
– Requires torque measurement.
Rivets
+ Fast.
+ Bonds different materials.
+ Removable.
– Stress concentration at rivet location.
– Inappropriate thermal expansion/contraction.
– Rivet protrudes from material surface.
– Difficult to remove.

Welding
+ Strong bond.
+ Immediate bonding.
+ Provides a tight seal.
– Limited to compatible metals.
– Requires preparation/finishing.
– Hazardous during operation (metal fumes, eye injury, burns).
– Increases susceptibility to corrosion or stress cracking.
Types of structural adhesives
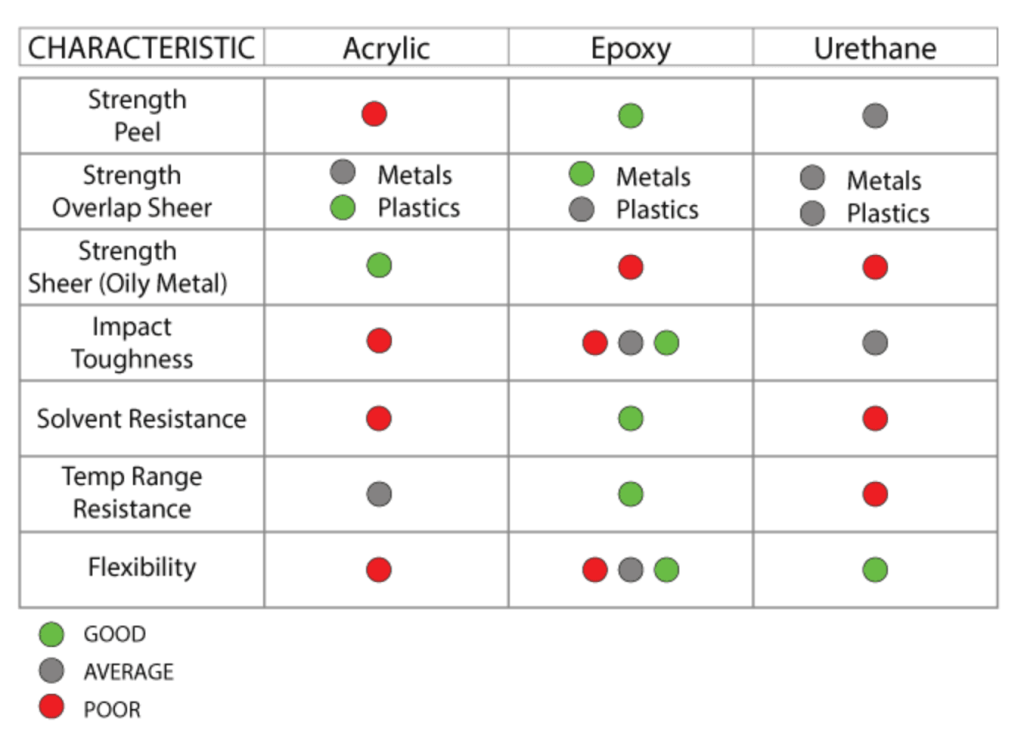
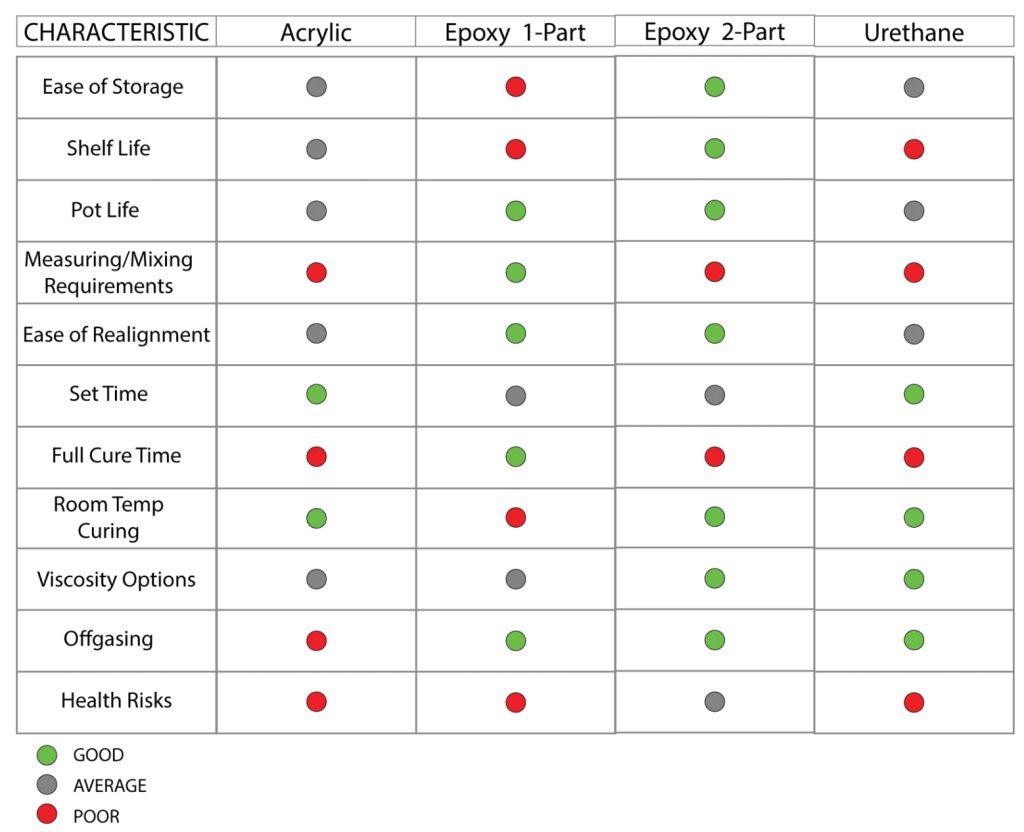
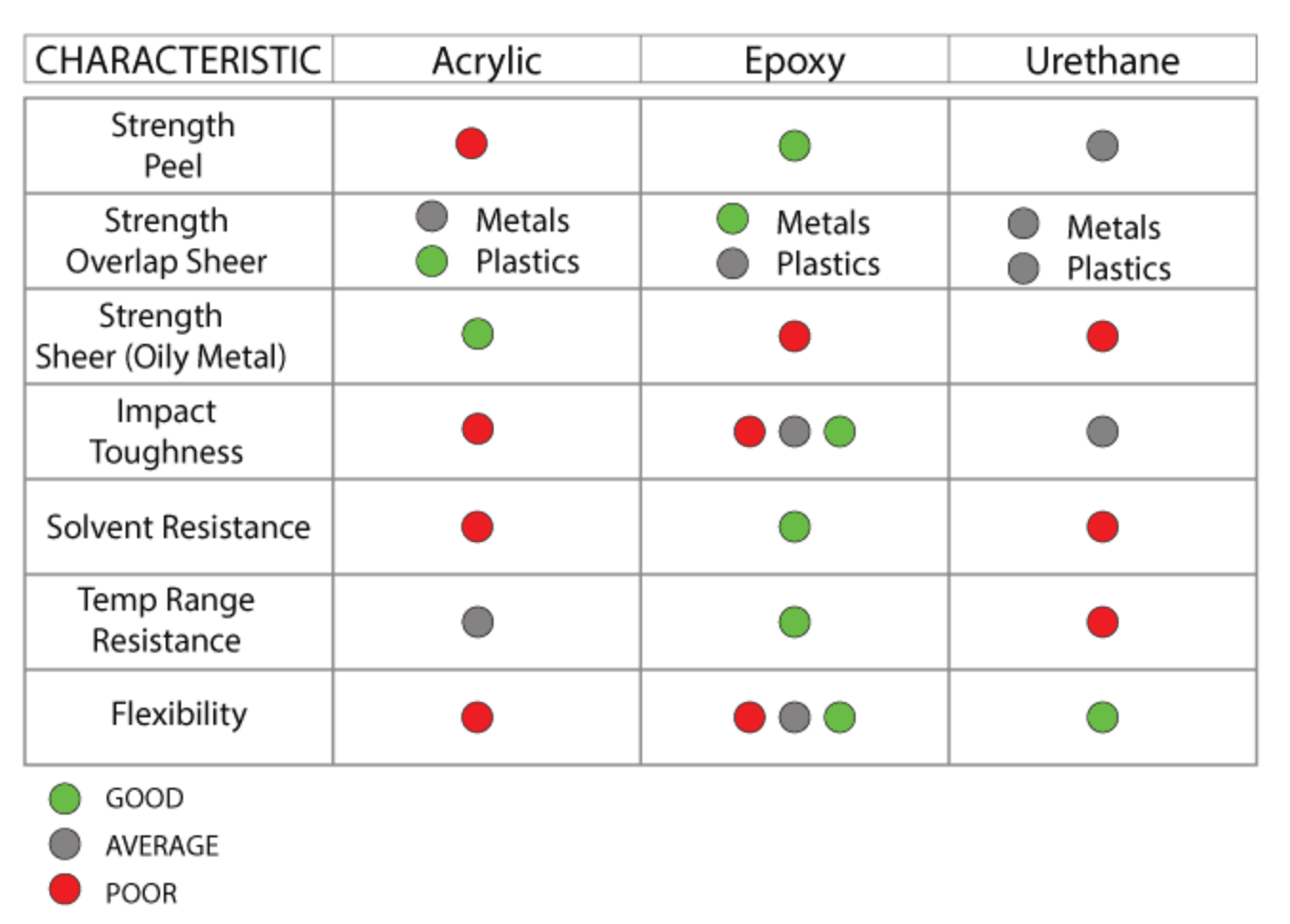
There are three types of structural adhesives commonly used for structural bonding applications: epoxy, acrylic, and urethane. The choice of adhesive depends on the materials to be bonded, the operating environment, and the technical specifications of the process.
Epoxy
Epoxy adhesive is an excellent choice for bonding similar and dissimilar materials, especially wood, metal, glass, ceramics, rigid plastics, and some types of rubber. Epoxy can create bonds with excellent heat resistance. Certain types of epoxy maintain bond integrity at temperatures up to 200°C. Epoxy adhesives are also quite strong (some with shear strength exceeding 5,000 psi) and resistant to chemicals. Structural epoxy adhesives are effective for repairing holes or cracks in metal, glass, and plastic components.
Epoxy structural adhesives are available in one or two-component forms. Epoxy is known to take a long time to cure and cure, but time can be reduced by choosing suitable methods such as heat or ultraviolet radiation.
Due to the need for mixing with resin and long drying times, epoxy can be difficult to implement in processes requiring short lead times.
Acrylic
Acrylic adhesive excels in bonding both similar and dissimilar substrates, although acrylic adhesives struggle with bonding plastics. Acrylics integrate easily into high-volume manufacturing processes, requiring minimal surface preparation, setting within 30 minutes, and drying in an hour or less.
Acrylic structural adhesives can even bond materials that are greasy or dirty, eliminating the need for thorough cleaning and surface preparation, though proper cleaning and surface preparation are still recommended for optimal bond strength.
Acrylics are not as strong or heat-resistant as epoxies; their maximum shear strength is around 3,500 psi, while the maximum operating temperature is below 100°C. Acrylics are also not as flexible as epoxies or urethanes, meaning acrylic bonds are more susceptible to damage under dynamic loads.
Urethane
Urethane is highly effective in bonding plastics and various materials, including metal to plastic and metal to glass, while being designed to provide superior durability. Urethane structural bonding is flexible and resilient against vibrations, shocks, and impacts.
Urethane adhesives come in various shear strengths, even up to 5,000 psi. However, urethanes are not easily integrated into complex processing lines because they take a long time to cure (up to 72 hours). Some may take even longer to cure due to cross-linking reactions. Care must be taken in storing and using urethane, as moisture can cause the adhesive to harden.
Two-Component Structural Adhesives
Two-component structural adhesives offer various processing speeds. Suitable for bonding all types of substrates, these flexible solutions allow better control over drying and curing times during application. Essentially, two-component structural adhesives allow curing at room temperature or through spray application in automated processes. This means safer and more efficient bonding while improving precision and aesthetics both during and after application.
Sealant
Sealant structural adhesives prevent pressure loss or fluid leakage as well as protect components against condensation and corrosion. Ideal for filling gaps between parts or sealing pipes, structural sealant adhesives provide excellent adhesion on various substrates, helping to narrow the gap between conventional sealants and adhesives. Applications can be done manually or automatically, and a range of different adhesive formulas allows for flexibility across various industrial and commercial designs.
Versatility of Structural Adhesives
Structural adhesives can be found in numerous applications in automotive assembly, bus, sleeper cab, door assembly, windows & architecture.




- Giải pháp Keo dán xe giường nằm
- Giải pháp keo Bostik cho xe buýt & xe khách
- Keo công nghiệp dán xe tải đông lạnh
- Keo dán cửa nhôm, cửa sổ nhôm kính
- Keo dán kính mặt dựng toà nhà (FACADE) chất lượng cao & tối ưu chi phí
The outstanding advantage of structural adhesives is their ability to bond both high-energy surface materials (e.g., metals, oxides, ceramics) and low-energy surface materials (e.g., rubber, plastics, composites).
Epoxy is best for similar or closely matched high-energy surface materials, while urethane excels in bonding different substrate materials. Acrylic provides bonding solutions for any remaining challenges. Acrylic can even bond materials with extremely low surface energy, including various types of polypropylene and polyethylene.
Process engineers highly appreciate the effectiveness that structural adhesives bring. Structural adhesives are easier to apply to substrates and consume less time compared to installing screws or welding.
Structural adhesives also require minimal preparation when dealing with metal or plastic substrates. Surface cleaning is as simple as wiping with isopropyl alcohol. Aluminum oxidizes quickly, but a chromate primer or anodizing layer can prevent corrosion. Difficult-to-bond plastics can be improved by treating with primers, plasma, or simple abrasion.
Structural adhesives offer high aesthetic appeal and noise reduction. Instead of protruding hardware or recessed surfaces to hide bolt heads or weld seams, structural adhesives provide clean, paintable, or bondable surfaces. Materials bonded tightly or welded tend to emit squeaky noises, which is not an issue with adhesives.
The drawbacks of structural adhesives are minimal. Adhesive bonds are permanent, so reworking parts that have been bonded is almost impossible, although there are exceptions. Most adhesives emit fumes, so ventilation or worker protection is necessary. Some products may cause skin irritation and require careful handling techniques. However, there is no risk of burns, as with welding, or getting caught in machinery, as with screws.
The benefits of structural adhesives
Designed for a wide range of technical applications across various industries, structural adhesives provide reliable and long-lasting bonding and sealing capabilities, ideal for applications requiring load-bearing capacity and other structural conditions.
The benefits of structural adhesives include:
- Substantial elimination or reduction of costly mechanical methods.
- Improved aesthetics compared to mechanical screws.
- Even weight distribution across surfaces.
- Multi-substrate bonding: bonding different substrate materials.
- Fast processing speed.
- Ideal for weight reduction or lightweight applications.
- Reduced labor costs.
- Filling large gaps between components.
Structural adhesives in the automotive industry
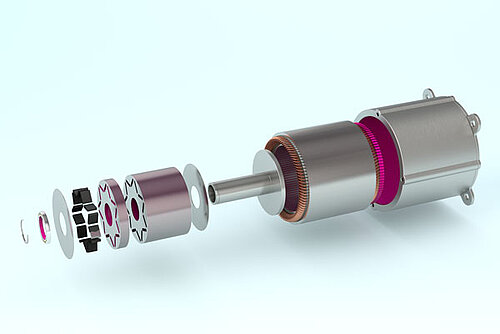
Meeting automotive-related testing requirements:
- Helps make vehicles lighter.
- Increases vehicle durability.
- Reduces noise levels.
- Enables lightweight design through multi-material bonding.
- Energy-saving with UV curing process.
Structural adhesives are widely used for bonding tasks in the automotive industry, from vehicle bodies to electric motor magnets and screen frames. High-temperature resistance, strong bonding capability ensures excellent durability throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle.
Hitta structural adhesives meet OEM and supplier requirements, ensuring passenger safety through the balanced tensile strength properties of safety-related components.
Contact information
Please contact Hitta to receive detailed consultation from our specialists regarding structural adhesive solutions that are compliant and suitable for your business processes, helping to optimize costs and significantly increase efficiency.
- ☎️ Hotline: 0565.336.879.
- ✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn