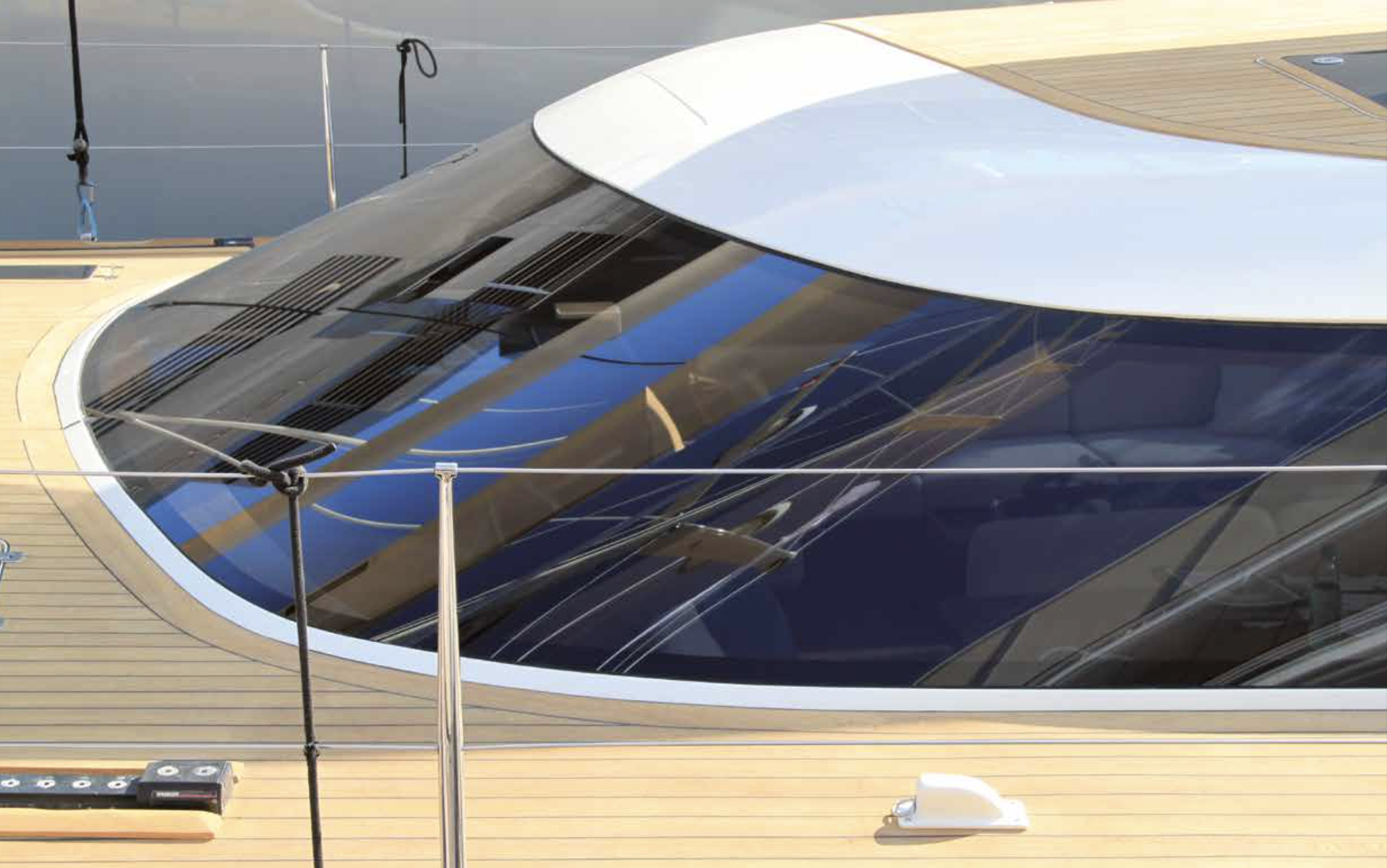
Nowadays, ships and yachts are following the design trends of modern buildings with glass designs everywhere. This requires new and more advanced material bonding solutions. Additionally, there is a difference between bonding yacht glass/windows compared to the glass/windows/facades of a building, as yachts rely on glass installation to maintain the separation between the interior of the vessel and water, as well as other harsh weather elements. If glass installation is not successful, the vessel is prone to water ingress and may easily sink or capsize. This is where Hitta’s advanced adhesive solutions come into play.
Types of glass used on ships and yachts
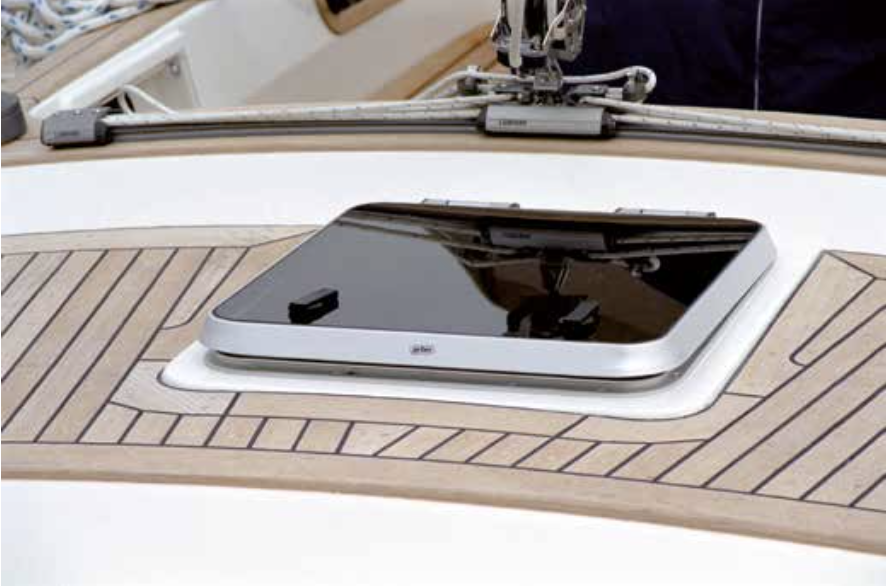


There are various types of glass used for windows and portholes on ships and yachts. All these types are installed and sealed using the same method, applying industrial adhesive to achieve durable and high-quality results. The types of glass include:
- Solid Glass.
- Multi-layered Glass.
- Polycarbonate Glass.
- Acrylic Glass (PMMA).
- Chemically or thermally Toughened Glass.
- Curved Glass varieties.
Recommended products
Methods for bonding windows/glass
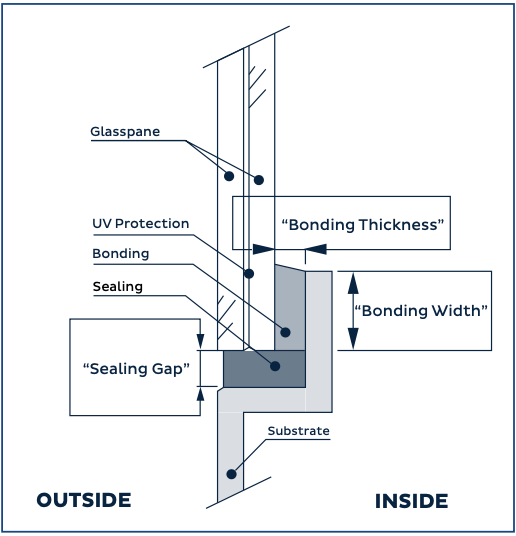
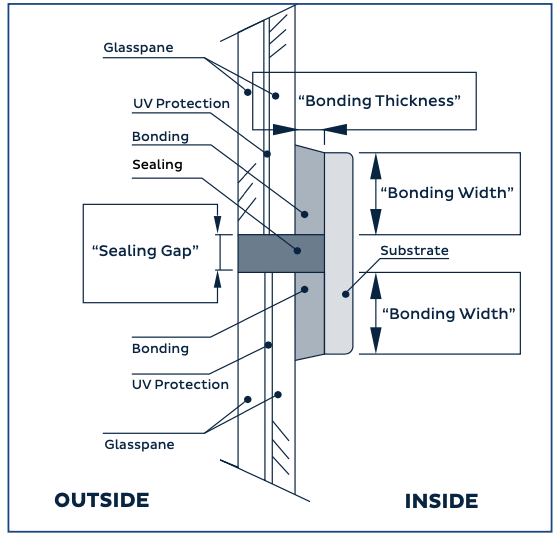
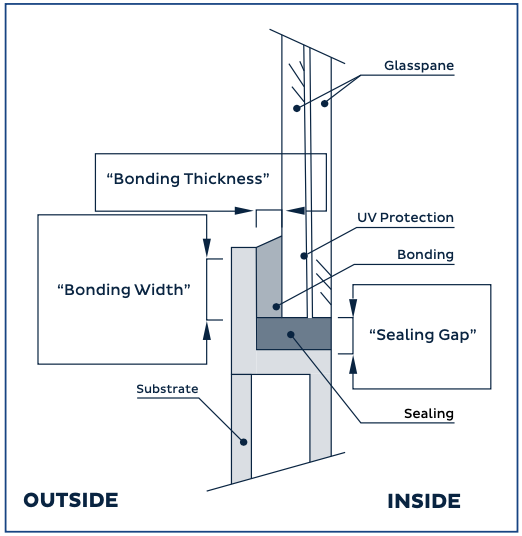
Note:
- Outside: Refers to the external side of the glass or window.
- Inside: Refers to the internal side of the glass or window.
- UV protection: Indicates protection against ultraviolet (UV) rays.
- Glass pane: The individual piece of glass.
- Bonding: Refers to the process of adhering or sealing the glass to another surface using adhesive or sealant.
- Bonding thickness: The thickness of the adhesive or sealant used in bonding.
- Bonding width: The width of the adhesive or sealant applied in bonding.
- Sealing: The process of sealing or caulking around the edges of the glass to prevent water or air infiltration.
- Sealing gap: The space or opening between the glass and the surrounding frame where sealing or caulking is applied.
- Substrate: The underlying material or surface onto which the glass or window is mounted.
Requirements for bonding glass on ships and yachts
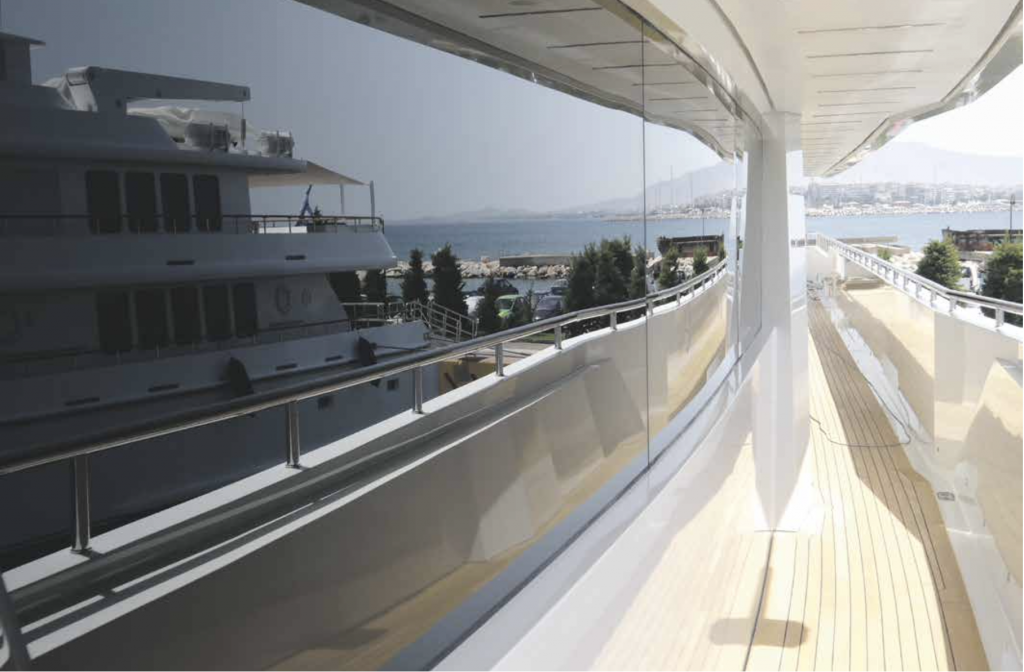

Elastic Joint:
An elastic joint is considered to be flexible if the joint has the ability to transmit forces and distribute stress evenly. Furthermore, the joint exhibits high elasticity (ability to return to its original shape after deformation). The main purpose is to hold the glass panel in place and maintain adhesion to the ship’s structure (transmitting loads from the glass panel to the ship’s structure). Additionally, the elastic joint will seal the ship’s interior from water and other weather elements while allowing for expansion/contraction of the glass and/or supporting structure.
Joint dimensions:
- Joint thickness: The distance between surfaces.
- Joint width: The distance between the substrate and adhesive surfaces, between the adhesive and the facade.
Gap filling: In the case of flat or recessed glass installation, the gap is the distance between the edge of the glass and the adjacent substrate layer, measured on the glass plane.
UV protection: The adhesive and sealant need to have very high UV resistance, as UV rays degrade the chemical composition, leading to deterioration.
Substrate Preparation
The dimensions of the joint need to be calculated accurately. All areas to be bonded must be cleaned with a dry, lint-free, colorless cloth, using specialized cleaning solution. Drying time is 5 minutes, maximum 6 hours.
For glass/windows with ceramic coating:
Pre-treat the frame and coating with a dry, lint-free, colorless cloth wetted with specialized solution, wiping in one direction to avoid surface runoff. Drying time is 5 minutes, maximum 6 hours.
Pre-treat the edges of the window with specialized solution using appropriate tools. This way, the sealing part will be protected from UV rays. Drying time is 5 minutes, maximum 24 hours.
For glass/windows without ceramic coating:
Apply specialized solution to create a certain layer on the surface and on the window edges. Drying time is 5 minutes, maximum 24 hours.
Ensure that the applied solution has the appropriate dimensions to prevent UV rays from penetrating the bonding surface.
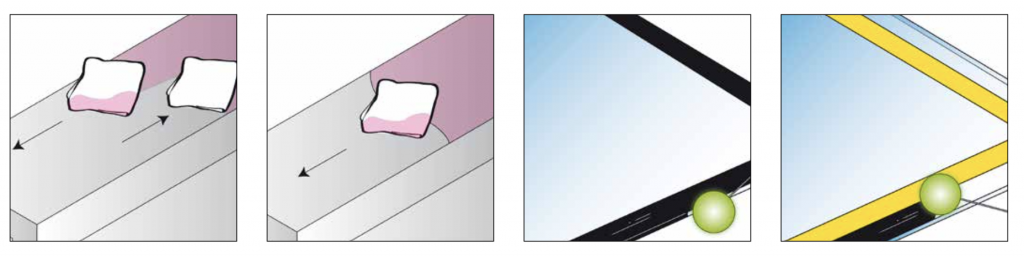
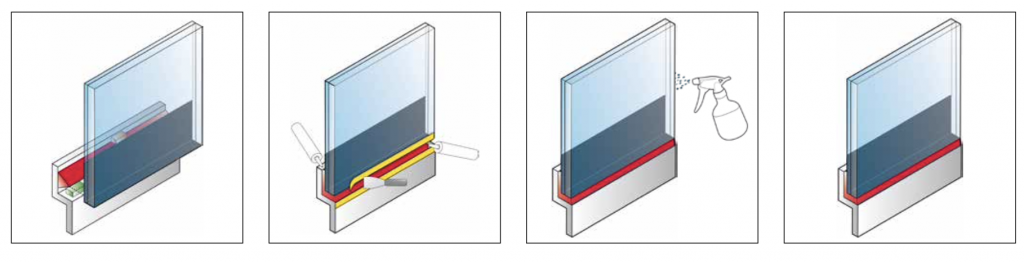
Window/Glass Bonding
- Use spacer blocks to control the size of the sealing/filling & bonding line.
- Temperature must be between +5°C and +35°C, with maximum relative humidity of 75%.
- Use supports to prevent windows/glass from sliding.
- Apply adhesive & sealant.
- Place the window/glass into the frame and push until the proper gap is achieved.
- After 24 hours at a minimum temperature of 23°C and 50% RH, the windows can be tightly closed.
- Avoid allowing condensation on the bonding line; it is recommended to seal the windows from the inside.
Window/Glass Sealing
- During curing, the sealant needs to be protected from direct sunlight and rain. Temperature must be between +5°C and +35°C, with relative humidity from 40% to 75%.
- Cut the sealant/adhesive nozzle to match the width of the joint.
- The joints must be filled from bottom to top to prevent air voids. The nozzle should be placed at the bottom of the joint, the gun held at a 60° to 80° angle. Pull the nozzle at a constant speed through the joint.
- Clean the outside of the window with specialized cleaning solution using a dry, lint-free, colorless cloth.
- Apply adhesive tape on both sides of the joint.
- Apply the adhesive to the joint, avoiding trapped air bubbles.
- Once the joint is sealed, a spatula can be used to flatten the joint and remove excess sealant/adhesive.
Contact information
Hitta specializes in providing various types of industrial-grade adhesives and tapes for both industrial and commercial sectors. Contact us for the most cost-effective and efficient solutions.
- ☎️ Hotline: 090.8611.011 (Mr. Dương).
- ✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn




