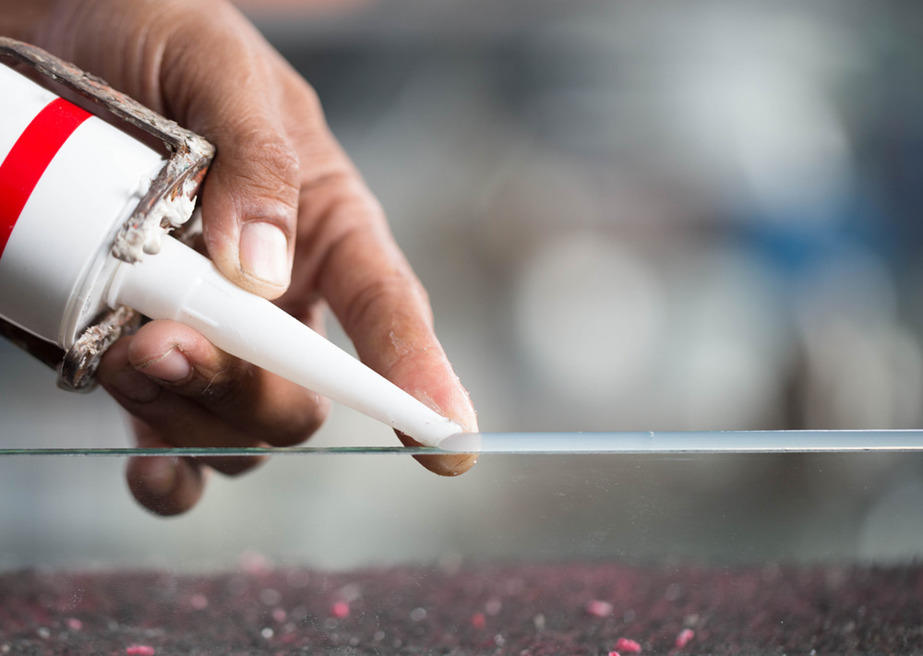
Industrial adhesives are used in the manufacturing and assembly of components across various industrial sectors, making products lighter, safer, and more durable. They also enhance the manufacturing process by saving time and costs, helping businesses operate efficiently, competitively, and sustainably.
When to use Acrylic Adhesive?
Acrylic adhesives are primarily used to bond various materials such as plastics, glass, or wood to metal. Acrylic adhesives have good resistance to friction and wear but are not as strong as epoxy adhesives. However, acrylic bonding agents are typically cheaper than epoxy ones. The curing time of one-component acrylic adhesives is relatively long, ranging from 5 to 30 minutes, but it can be accelerated by heating.
When to Use Epoxy Adhesive
Epoxy adhesive is a chemical compound commonly used for bonding components. Epoxy is a copolymer, formed from two different chemical substances including the adhesive and the hardener.
Use acrylic adhesive when a high mechanical strength bonding agent is needed, whether it’s for impact resistance, cutting, or peeling. Epoxy adhesive is available in one or two-component forms.
If using a one-component adhesive, epoxy undergoes a polymerization reaction within the polymer chain (making the adhesive harden) when exposed to heat, typically in the range of 100 to 200 °C. When using this type of adhesive, an oven or infrared machine, or at least a heat gun, should be available to induce polymerization (the drying and hardening process of the adhesive) which may take from 30 minutes to 2 hours. One-component epoxy adhesive can substitute for welding.
If there’s no heat source for the polymerization reaction, two-component epoxy adhesive can be used, which offers the advantage of allowing the adhesive to harden at room temperature, and this process can also be accelerated with heat.
It’s important to choose epoxy adhesive based on the required properties, such as transparency and flexibility when needed, large gap between assembled parts, etc.
Epoxy adhesive can be categorized into three types when cured:
- Hard type: has excellent resistance to cutting forces and very good durability. This type of epoxy is particularly used with hard substrates and high static charges.
- Soft (flexible) type: has good impact resistance and peel resistance, and can withstand low temperatures. This epoxy type is especially used to bond different materials with different coefficients of expansion.
- Strong bonding type: this is a combination of the above two types.
When to Use Polyurethane & Urethane Adhesives?
Polyurethane adhesives are widely used in the construction industry, such as for bonding insulation panels. They are highly flexible adhesives, but have limited mechanical strength compared to epoxy adhesives, especially at high ambient temperatures.
Polyurethane adhesives cure by reacting with moisture in the surrounding environment and can be applied using a heat gun to reduce curing time. If humidity is low, it’s better to use two-component polyurethane adhesive.
Urethane adhesive is mainly used for bonding or repairing materials made from rubber.
When to Use Cyanoacrylate Adhesive?
Cyanoacrylate adhesives come in liquid or gel form. These adhesives are primarily designed for rapid bonding and they provide good shear strength. At room temperature, the curing (drying) of the adhesive is almost instantaneous.
The common type of cyanoacrylate adhesive is the liquid adhesive, perfectly suitable for bonding rigid materials. Nowadays, there are many variations of cyanoacrylate adhesive in gel form with viscosity ranging from medium to high.
Liquid adhesive can be applied to elements, components assembled by capillary action, diffusion adhesive due to the effect of capillarity. On the other hand, gel is particularly suitable for vertical surfaces and porous materials.
Cyanoacrylate adhesive only bonds to one surface if there is moisture. Thus, if the surface is completely dry, it won’t be effective as it won’t create adhesion. To address this issue, a thin layer of water can be applied to the surface to initiate curing.
Cyanoacrylate adhesive is used to bond metal components, glass fibers, ceramics, hardcovers, rubber, and plastics. It should be noted that for heat-resistant plastics, epoxy resin should be preferred.
The disadvantage of cyanoacrylate adhesive is its low impact resistance and low heat resistance.
When to Use Silicone Adhesive?
Silicone adhesive is a flexible adhesive with high resistance to dynamic stress and excellent sealing ability. Silicone adhesive also has good resistance to solvents, UV radiation, and high temperatures. However, its mechanical strength is not very high. One-component silicone adhesive requires high moisture content to cure. If the humidity is low, it’s better to use two-component adhesive.
Resistance capabilities of silicone adhesive include:
- Dynamic interaction forces.
- Solvents.
- UV radiation.
- High temperatures.
-
 Adhesive for aluminum door corners, aluminum frame windows, aluminum flash doors | Bostik Aluseal
Adhesive for aluminum door corners, aluminum frame windows, aluminum flash doors | Bostik Aluseal -
 Bostik N310 Multi-Purpose Construction Adhesive
Bostik N310 Multi-Purpose Construction Adhesive -
 Bostik H505 – transparent sealant & adhesive
Bostik H505 – transparent sealant & adhesive -
 Bostik P310 – expanding foam adhesive for thermal insulation and sound reduction
Bostik P310 – expanding foam adhesive for thermal insulation and sound reduction -
 Bostik H725 hybrid adhesive designed for facade cladding and expansion joints
Bostik H725 hybrid adhesive designed for facade cladding and expansion joints -
 Bostik S736 Premium, Neutral Grade, High Modulus Silicone for Glazing & Facade Applications
Bostik S736 Premium, Neutral Grade, High Modulus Silicone for Glazing & Facade Applications -
 Bostik S551 – neutral silicone for gutters and roofs
Bostik S551 – neutral silicone for gutters and roofs -
 Bostik P795 – sealant for filling large gaps
Bostik P795 – sealant for filling large gaps -
 Bostik P590 – sealant for construction & expansion joints
Bostik P590 – sealant for construction & expansion joints -
 Bostik A330 FILL A GAP FLEX
Bostik A330 FILL A GAP FLEX -
 Bostik S546 Silicone – moisture resistance and waterproofing
Bostik S546 Silicone – moisture resistance and waterproofing -
 Bostik H360 hybrid sealant for construction & glass façade
Bostik H360 hybrid sealant for construction & glass façade -
 Bostik H785 – No more screws, Instant Adhesive
Bostik H785 – No more screws, Instant Adhesive -
 Bostik 7575
Bostik 7575 -
 Bostik S548
Bostik S548 -
 Bostik 7003
Bostik 7003 -
 Bostik 7008
Bostik 7008
When to Use 2-Component Adhesive?
Regardless of the type of adhesive, two-component adhesives have the advantage of not relying on surrounding conditions for curing, and the curing time of the two-component adhesive is well-controlled as long as the mixture is accurately proportioned.
Mixing can be done manually or automatically. Some two-component adhesives may produce more or less hazardous emissions, so it’s preferable to use them in well-ventilated areas.
Choose the appropriate industrial adhesive
| Adhesive | Compatible Materials | Application Form | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | Glass; Metal; Concrete; Wood; Rubber; Ceramic; Pottery; Leather; Polycarbonate; Polyester; Rigid PVC; Polyurethane; | Film; Bonding; One or two-component liquid; Thermal | Good shear and tensile strength; Excellent resistance to harsh temperatures; Good chemical resistance; Reversible bonding ability; Lack of flexibility; Poor UV resistance. Shrinkage during polymerization; Expensive. | Aerospace; Automotive; Electronics; Maritime; |
| Acrylic | Metal; Polycarbonate; Polyamide; Polyester; Plastics; | Two-component Bonding | Good tensile and shear strength; Good gap filling ability. | Mechanical Engineering |
| Cyanoacrylate | Plastics; Polymers; Metals; Glass fibers; Ceramic; Stones; Rubber | Rapid Installation | Rapid installation (around 10 seconds); The curing process is facilitated by good ambient moisture conditions. | Mechanical; Prototyping; Electronics. |
| Polyurethane | Glass; Wood; Rubber | Quick bonding; One or two components | Flexible bonding; Inhomogeneous bonding; Large surface area; Moisture-resistant; By using one-component adhesive, the adhesive will copolymerize with high moisture (slow curing); Good chemical resistance; Good heat resistance up to 90 °C. | Automotive; Carpentry. |
| Urethane | Rubber; Neoprene | Slow bonding; Expanding adhesive; One-component glue | Inhomogeneous bonding; Flexible assembly; Waterproof. | |
| Silicone | Glass; Concrete; Wood; Rubber; Ceramic; Pottery; Metal; Polyamide; Polyurethane | One-component adhesive | Bonding glass to various materials; High moisture polymerization adhesive (slow curing). Good sealing; Good weather resistance; Good solvent resistance. | Carpentry; Construction. |
| Methacrylate | Plastics; Metals; Thermoplastic; Polymer; Synthetic materials; Wood | Two-component; Transparent glue; Room temperature bonding; Rapid bonding | Transparent bonding; No need for surface pretreatment; Available in rigid, semi-rigid or flexible forms; Inhomogeneous bonding; High mechanical strength; Good impact resistance; Good low temperature resistance (down to -40 °C). | Aerospace; Automotive. |
Contact us
Hitta specializes in providing various types of specialized adhesives and tapes for both industrial and commercial sectors. Contact us for advice on the most effective solutions at the lowest cost:
- ☎️ Hotline: 090.8611.011 (Mr. Dương).
- ✉️ Email: hittajsc@hitta.vn
Solutions you may be interested in:
- Heat-resistant adhesive & high-temperature adhesive
- What are waterproof adhesives and sealants? Which type of adhesive is good?
- Bostik’s adhesive solutions for buses and coaches
- Bostik and everything you need to know
- Adhesive for bonding aluminum to aluminum, wood, concrete & other building materials
- Adhesive solution for coach, sleeper bus, transit vehicle, tourist car
- Adhesive for ship and yacht glass